Appearance
酰氯(Acid Chloride)
- 贡献者:彭玉婷;整理:陈宇暄
See also the above section about the reaction of acids, as acid chlorides are frequently not isolated but used immediately after formation.
参见上面关于酸的反应部分,因为酰氯通常不被分离,而是在形成后立即使用。
肖顿-鲍曼反应(Schotten–Baumann Reaction)
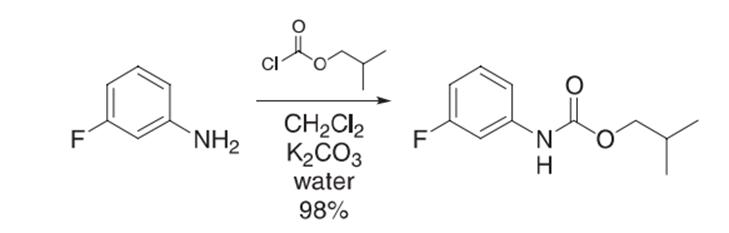
The Schotten–Baumann reaction is one of the most effective methods of converting acid chlorides to amides or chloroformates to carbamates. The workup typically involves separating the phases, drying the organic layer, and concentrating.
肖顿-鲍曼反应是将酸性氯化物转化为酰胺或氯甲酸酯转化为氨基甲酸酯的最有效方法之一。检查通常包括分离相,干燥有机层,和浓缩。
To a solution of 3-fluoroaniline (50.0 g, 450 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (200 mL) was added a solution of potassium carbonate (46.9 g, 339 mmol) in water (200 mL) at room temperature. The mixture was warmed to 32 ºC, and isobutyl chloroformate (66.2 g, 485 mmol) was added over 13 min while maintaining the temperature at 30−35 ºC. The mixture was stirred at 30−35 ºC for 2.5 h until complete by GC analysis. Aqueous ammonia (29.3 wt%, 7.2 mL, 111 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred at 30−35 ºC for 15 min. The mixture was cooled to 25 ºC and the pH adjusted from 8.7 to 1.9 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The phases were separated, and the aqueous layer was washed with CH2Cl2 (100 mL). The combined organics were washed with water (200 mL), and the water was back-extracted with CH2Cl2 (100 mL). Typically, the crude product was carried into the next step but, if desired, crystallization at this point from heptane at −30 ºC afforded the amide (93.1 g, 98.1%).
在3-氟苯胺(50.0 g,450 mmol)二氯甲烷(200 mL)溶液中加入碳酸钾(46.9 g,339 mmol)水(200 mL)溶液。将混合物加热至32ºC,加入氯甲酸异丁酯(66.2 g,485 mmol),超过13 min,同时将温度保持在30−35ºC。将混合物在30−35ºC下搅拌2.5 h,直到GC分析完成。加入氨水溶液(29.3 wt%,7.2 mL,111 mmol),在30−35ºC下搅拌15 min。将混合物冷却到25ºC,用浓盐酸将pH从8.7调整到1.9。分离相,用二氯甲烷(100 mL)洗涤水层。结合后的有机物用水(200 mL)洗涤,用二氯甲烷(100 mL)反提水。通常情况下,粗产物进入下一步,但如果需要,在−30ºC下从庚烷结晶得到酰胺(93.1 g,98.1%)。
参考文献: Herrinton, P. M.; Owen, C. E.; Gage, J. R. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2001, 5, 80–83.